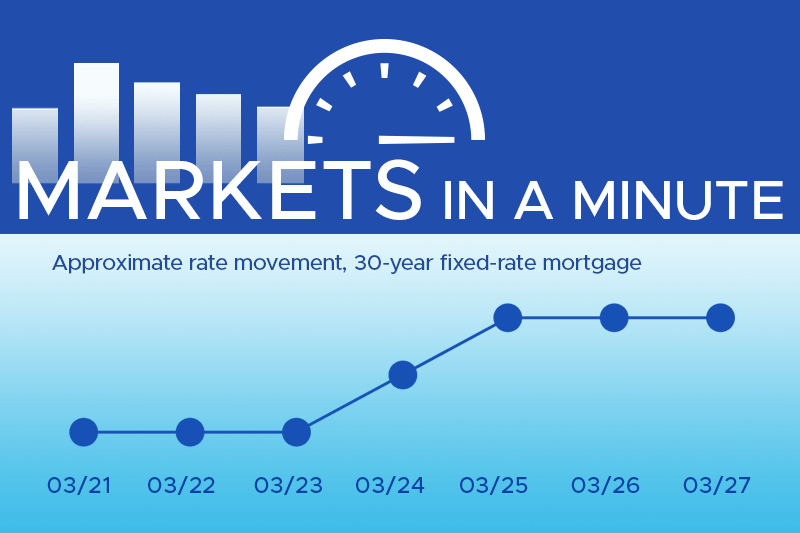
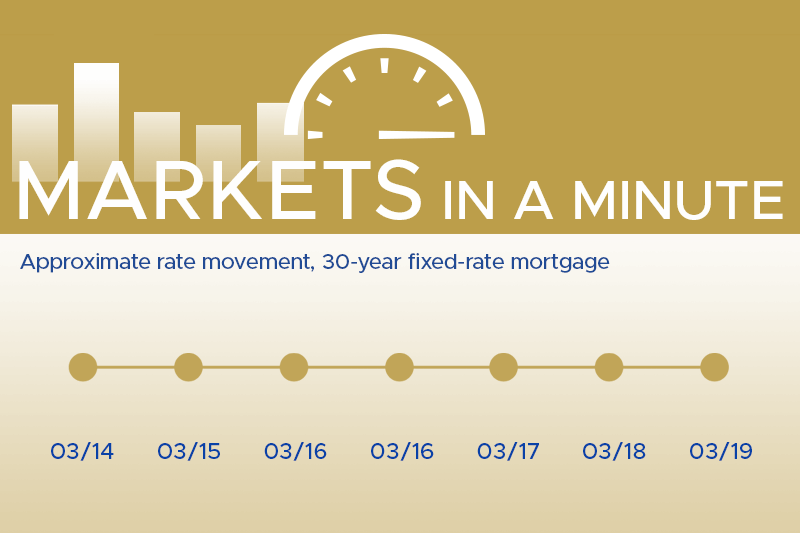At Thompson Kane, we stay ahead of shifting market trends so you don’t have to.…
How the Economy Affects Mortgage Rates
Mortgage rates are influenced not just by personal factors like credit scores and down payments but also by broader economic conditions. Factors such as inflation, unemployment, and decisions by the Federal Reserve can significantly impact the rates available to homebuyers and refinancers. Understanding these factors can help you make more informed decisions when it comes to securing a mortgage.

Inflation: A Key Driver of Mortgage Rates
Inflation, the rise in prices over time, reduces the purchasing power of money. When inflation is high, lenders raise mortgage rates to protect themselves from receiving less valuable future loan repayments. Conversely, when inflation is low, lenders are more comfortable offering lower rates.
For prospective buyers and those refinancing, tracking inflation trends can help you lock in a better mortgage rate during times of lower inflation.
Unemployment and Economic Growth: Push and Pull on Rates
The state of the job market affects mortgage rates as well. When unemployment is low and the economy is growing, demand for homes increases, which can push rates higher. On the flip side, when unemployment rises and economic growth slows, demand for mortgages typically drops, and lenders may lower rates to encourage borrowing.
During these times, the Federal Reserve often lowers interest rates to boost economic activity, which can result in lower mortgage rates and more favorable terms for buyers.
The Federal Reserve’s Influence
The Federal Reserve doesn’t directly set mortgage rates, but its policies play a significant role. By adjusting the federal funds rate—the rate at which banks lend to each other—the Fed influences borrowing costs across the economy, including mortgage rates.
When the Fed raises rates to combat inflation, mortgage rates tend to rise as well. When the Fed lowers rates to stimulate the economy, mortgage rates usually follow suit, giving buyers and refinancers an opportunity to secure lower rates.
Global Events and Market Sentiment
Global economic events can also affect mortgage rates. For example, trade tensions, geopolitical risks, or market uncertainty may drive investors toward safer assets like U.S. Treasury bonds. This shift can lead to lower long-term interest rates, including mortgage rates, even if domestic conditions remain stable.
Being aware of these trends helps borrowers take advantage of rate drops caused by external factors beyond the U.S. economy.
Key Takeaways for Homebuyers
Understanding how inflation, unemployment, and Federal Reserve actions affect mortgage rates can help you time your decisions more effectively:
- Low inflation generally means lower mortgage rates.
- Higher unemployment or slower growth often leads to lower mortgage rates as lenders respond to decreased demand.
- Federal Reserve interest rate decisions provide insights into future rate movements.
Your Thompson Kane home loan expert is here to help you navigate these complexities and find the best mortgage options for your situation. Whether you’re buying a home or refinancing, contact us today to explore current rates and opportunities.